How Does a 3D Printer Work?
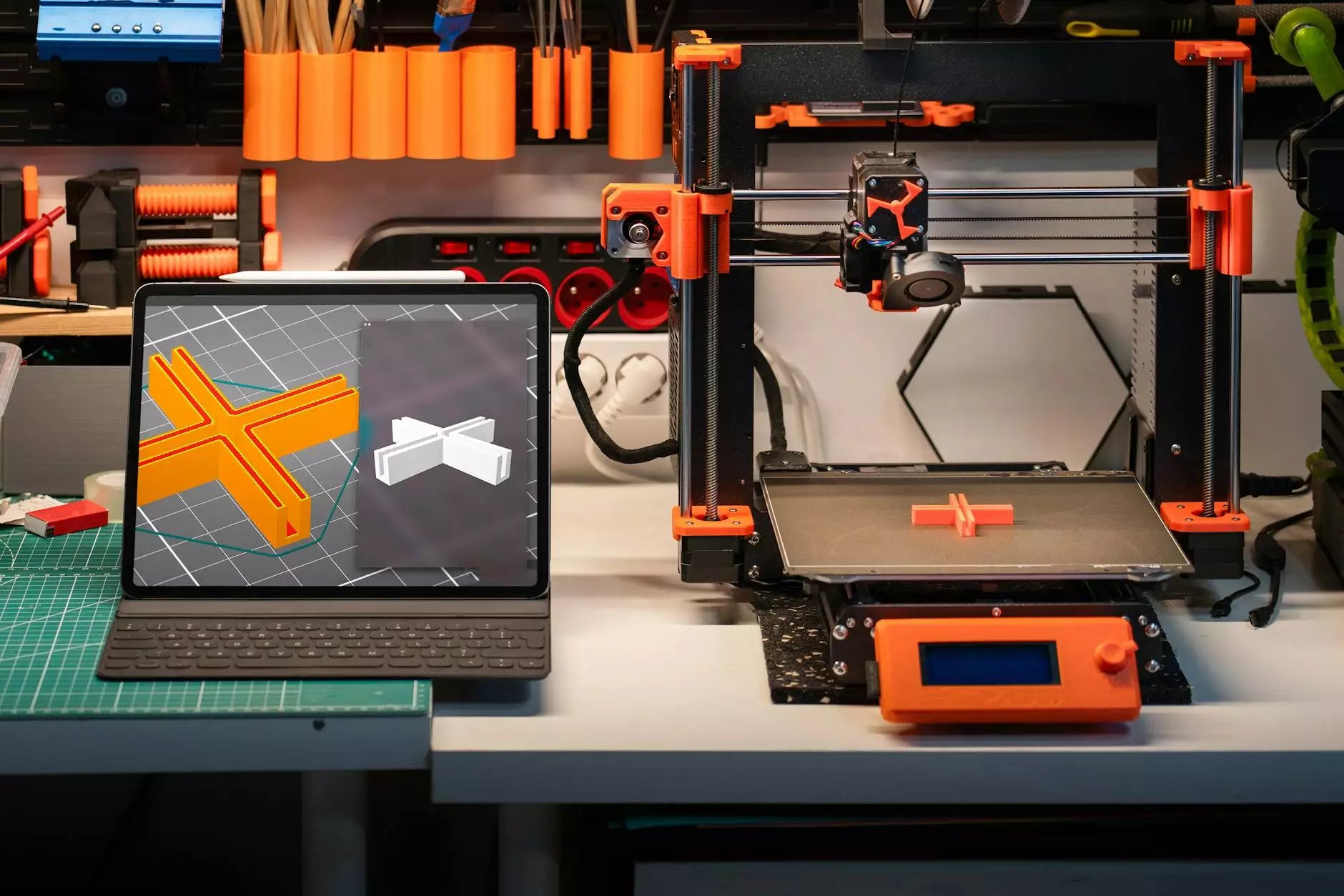

3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by enabling the creation of complex and intricate objects quickly and efficiently. This innovative technology has opened up a world of possibilities, allowing businesses to create prototypes, customized products, and even prosthetic limbs with ease. In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of a 3D printer and explore the processes involved in turning digital designs into physical objects.
Understanding the Basics
At its core, a 3D printer is a machine that builds objects layer by layer, using a digital design as a blueprint. The process starts with creating a 3D model using specialized software or scanning an existing object. The model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers, which the 3D printer uses as a guide to build the final object.
Components of a 3D Printer
A typical 3D printer consists of several key components:
- Frame: The frame provides stability to the printer and houses other components.
- Print Bed: This is the surface where the object is built. It can be heated to ensure better adhesion of the printing material.
- Extruder: The extruder is responsible for melting and depositing the printing material onto the print bed.
- Stepper Motors: These motors control the movement of the extruder and print bed, allowing precise positioning.
- Control Board: The control board coordinates the actions of various components and ensures smooth operation.
- Display: Some 3D printers come with a display that allows users to interact with the printer and monitor the printing process.
The Printing Process
Now that we have covered the main components of a 3D printer, let's explore the printing process itself.
1. Preparation
Before starting a print job, the user needs to prepare the 3D printer. This involves ensuring that the print bed is clean and level, and the extruder is properly calibrated. The user also needs to upload the digital design file to the printer, either via USB or an SD card.
2. Heating and Filament Loading
Once the printer is set up, it heats the print bed to the desired temperature (if required) and preheats the extruder. The printer then loads a filament, usually in the form of a spool, into the extruder. The filament is made from materials such as plastic, resin, or metal, depending on the printer's capabilities and the desired object's properties.
3. Printing the Object
With all the preparations complete, the actual printing process begins. The printer starts by depositing a thin layer of the molten filament onto the print bed, following the instructions from the sliced 3D model. As each layer is completed, the print bed lowers, allowing the printer to add the next layer. This process continues until the entire object is completed.
4. Cooling and Finishing
Once the object is fully printed, it undergoes a cooling process to solidify the material and ensure its structural integrity. After cooling, the object is ready for removal from the print bed. Depending on the complexity of the object and the filament used, additional post-processing steps such as sanding, painting, or polishing may be required.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing can be applied across various industries, offering numerous benefits and possibilities. Here are some key areas where 3D printing has made a significant impact:
Prototyping
One of the primary applications of 3D printing is rapid prototyping. It allows businesses to quickly iterate and test different designs without the need for expensive tooling. This saves both time and money, enabling faster product development.
Custom Manufacturing
3D printing enables the production of highly customized products. It allows businesses to create unique designs tailored to specific customer requirements. This level of customization can lead to increased customer satisfaction and competitive advantage in the market.
Medical Advancements
The field of medicine has greatly benefited from 3D printing technology. It has revolutionized the production of prosthetics, making them more accessible and cost-effective. Additionally, 3D printing has enabled the creation of patient-specific surgical models, helping surgeons plan complex procedures with precision.
Architectural Models
Architects and designers utilize 3D printing to create accurate and detailed architectural models. This allows clients and stakeholders to visualize concepts and make informed decisions about construction projects.
Education and Innovation
3D printing has become an essential tool in educational institutions and research centers. It allows students and researchers to explore complex concepts, test hypotheses, and develop practical skills in fields such as engineering, design, and material science.
Conclusion
3D printing is a fascinating technology that has transformed the way we manufacture objects. By understanding the inner workings of a 3D printer and its various processes, you can appreciate the incredible capabilities it offers. From personalized products to advancements in medicine, 3D printing continues to push the boundaries of what is possible. Embracing this technology can provide businesses with a competitive edge and unlock a world of creative opportunities.
how does a 3d printer work