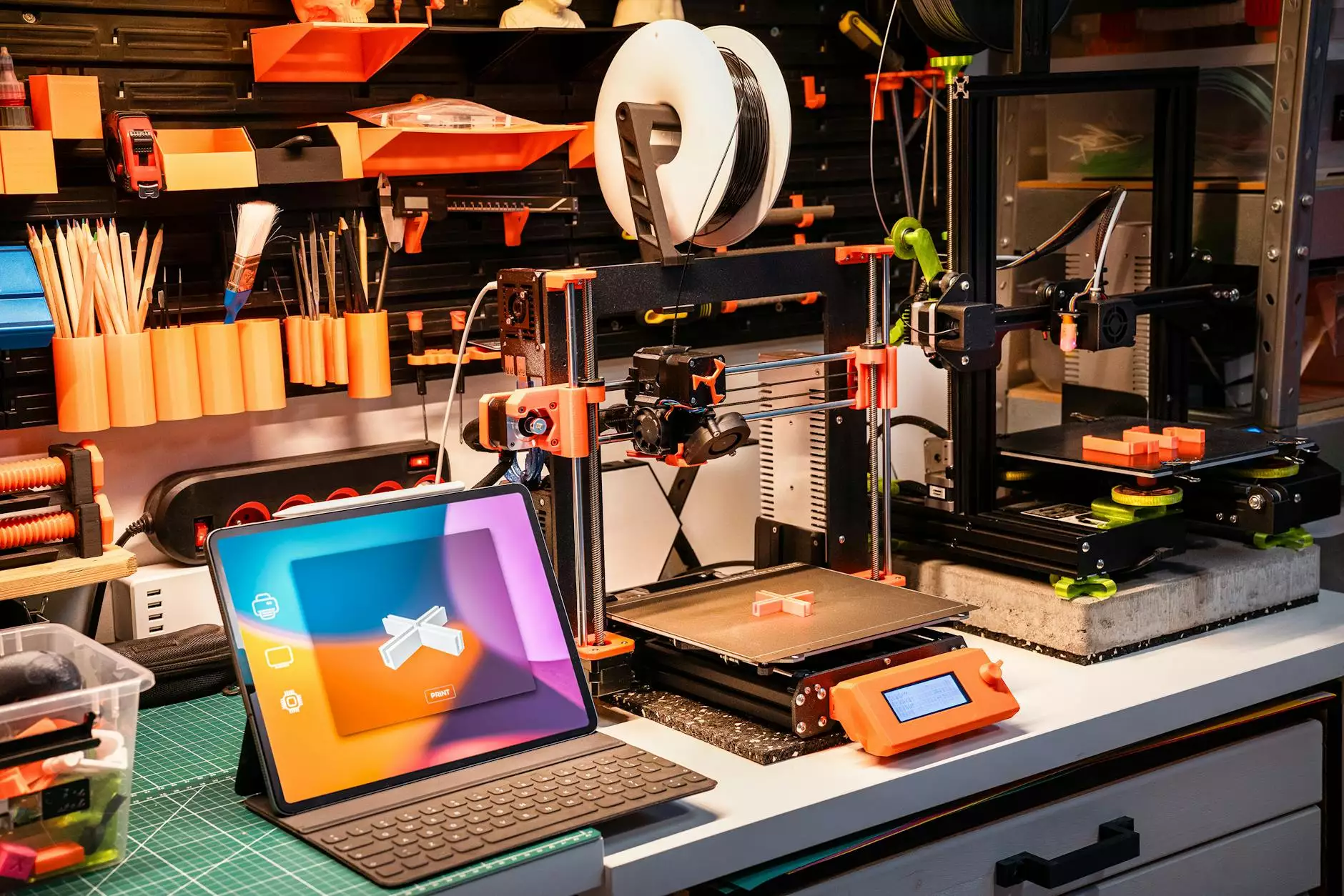
How Does a 3D Printer Work?

Welcome to SelfCAD.com, your go-to resource for all things related to IT Services & Computer Repair, Software Development, and 3D Printing. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of a 3D printer and shed light on the revolutionary technology that is shaping the future of manufacturing. By understanding how a 3D printer works, you'll gain insights into the immense capabilities of this cutting-edge device.
Introduction to 3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that involves creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials on top of each other. It is a revolutionary technology that has gained significant popularity in various industries, including architecture, aerospace, healthcare, and more. With a 3D printer, you can transform digital designs into physical objects with remarkable precision and intricate details.
The Components of a 3D Printer
A 3D printer consists of several key components that work together to bring your designs to life. These components include:
- 1. Print Bed: The print bed is the surface on which the object is built. It provides a stable foundation for the print process.
- 2. Extruder: The extruder is a critical part of a 3D printer that melts the printing material, known as filament, and deposits it layer by layer to create the object.
- 3. Hot End: The hot end is responsible for heating the filament and guiding it through the extruder.
- 4. Control Board: The control board acts as the brain of the 3D printer, interpreting instructions from the computer and controlling the movements of the printer's components.
- 5. Stepper Motors: Stepper motors provide precise control over the movement of the print head and other components.
- 6. Power Supply: The power supply provides the necessary electrical power to operate the printer.
- 7. Filament: Filament is the material used for 3D printing. It comes in various types, such as PLA, ABS, and PETG, each offering unique properties.
The Printing Process
Now that we have an overview of the main components, let's dive into the actual printing process of a 3D printer:
- Step 1: Design: Start by creating a digital 3D model of the object you wish to print. This can be done using computer-aided design (CAD) software or by downloading pre-made designs from online repositories.
- Step 2: Slicing: Once your design is ready, the next step is to prepare it for printing. This involves 'slicing' the 3D model into individual layers, each representing a specific height and shape of the object.
- Step 3: Material Loading: Load the filament of your choice into the 3D printer's extruder. Ensure that the filament matches your desired material properties and color.
- Step 4: Printing: Start the printing process and watch as the 3D printer brings your design to life. The printer will deposit the melted filament layer by layer onto the print bed, gradually building the object from the bottom up.
- Step 5: Cooling and Finishing: Once the printing is complete, allow the object to cool down before removing it from the print bed. Depending on the complexity of the design and the material used, you may need to perform additional post-processing steps such as sanding, painting, or polishing to achieve the desired finish.
Applications of 3D Printing
The versatility of 3D printing has led to its adoption in numerous fields. Some notable applications of 3D printing include:
- 1. Prototyping: 3D printing allows for rapid and cost-effective prototyping, enabling designers to iterate and refine their concepts quickly.
- 2. Manufacturing: Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare are utilizing 3D printing to create highly customized and complex components.
- 3. Education and Research: 3D printing is widely used in educational settings to enhance learning experiences and foster creativity. It also plays a crucial role in research, enabling scientists to create intricate models and prototypes for experimentation.
- 4. Art and Design: Artists and designers leverage 3D printing technology to push the boundaries of creativity and produce unique, intricate pieces.
Conclusion
3D printing is a truly remarkable technology that has the potential to revolutionize the world of manufacturing and design. By understanding how a 3D printer works and its applications, you can unlock endless possibilities and explore new horizons in creativity, innovation, and problem-solving. SelfCAD.com, a leading platform in the IT Services & Computer Repair, Software Development, and 3D Printing industries, is here to provide you with the necessary tools, resources, and knowledge to embark on your 3D printing journey.
Visit SelfCAD.com today and discover the captivating world of 3D printing!
how does a 3d printer work